Pile Testing
Pile tests are an effective and reliable method of identifying possible defects within new or existing building piles, bridge piles, concrete structures, or foundations.
Southern Geophysical have been conducting pile tests and data analysis throughout New Zealand and the Pacific Islands for 15 years. Testing is based on SESOC/NZGS Pile Construction Specification – Bored and Driven piles (June 2022) which references the relevant ASTM standards.
There are several pile testing methods that can be used. Southern Geophysical can determine which test method would be most suitable for a project from these methods:
Low Strain Pile Integrity Testing (LS-PIT)
Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL)
Singlehole Sonic Logging (SSL)
Parallel Seismic Testing
Low Strain Pile Integrity Testing (ASTM D5882)
Low Strain Pile Integrity Testing (LS-PIT) is a non-destructive testing method used to evaluate the integrity of deep foundation piles by measuring the response of the pile to a low strain impact. While the method is useful in obtaining pile integrity and shape information about a pile, the method has limitations as described in the ASTM standard D5882. One limitation is that the pile must differ from the surrounding material in density/Youngs modulus. If the pile being investigated is founded in a material with similar or the same density/strength, there will be no acoustic impendence change at the pile skin and the compressional wave generated at the impact point will simply “leak” into the surrounding rock mass rather than travel down the pile. In basic terms the surrounding rock will mean the pile being tested will appear as an infinitely wide pile invaliding the testing method.
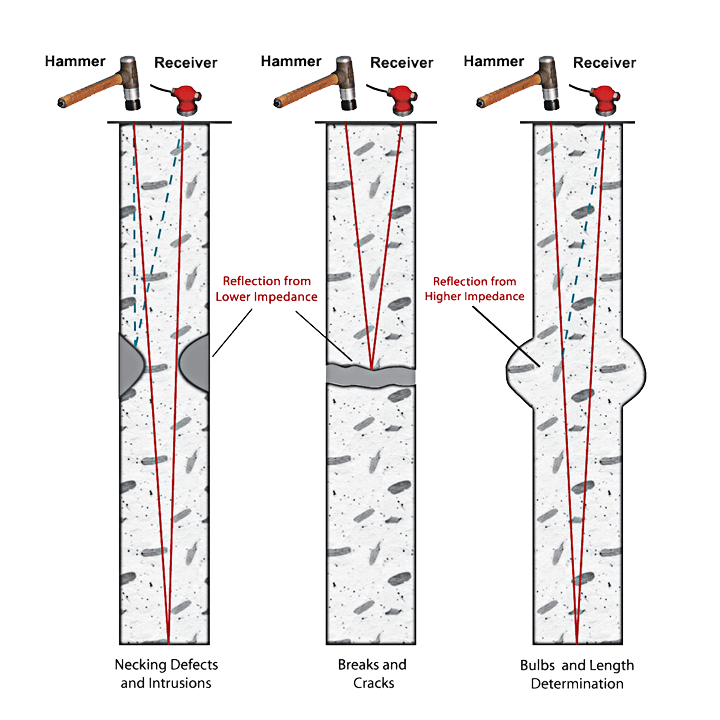
Image sourced from Olson Instruments, USA
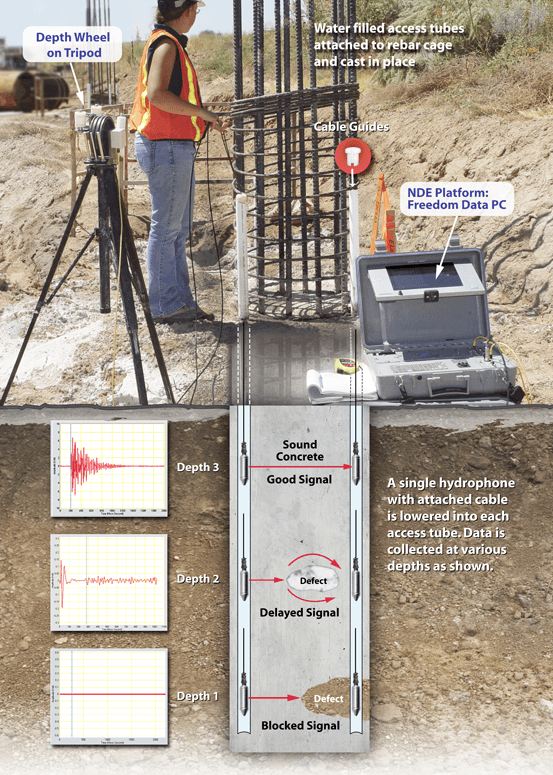
Image sourced from Olson Instruments, USA
Crosshole Sonic Logging (ASTM D6760)
Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL) is an accurate and reliable technique for assessing the integrity of deep foundation elements constructed on-site from concrete or grout. The Crosshole Sonic Logging method is normally applied as a quality assurance technique for newly placed drilled shafts and auger cast piles.
CSL testing provides assurance that the foundation concrete is sound and contains no defects, such as soil intrusions, necking, sand lenses, voids, foreign inclusions etc. The extent, depth, and approximate lateral location of defects can be determined with the CSL method. The CSL method is typically performed in steel access tubes tied to the rebar cage and cast into the shaft at the time of construction.
Singlehole Sonic Logging (ASTM D6760)
The single hole sonic logging method is used in cases where only a single access tube can be placed in a shaft and tests the concrete quality in the region around the single access tube. The access tube must be made of plastic, and testing must be conducted as soon as practical to avoid debonding issues.
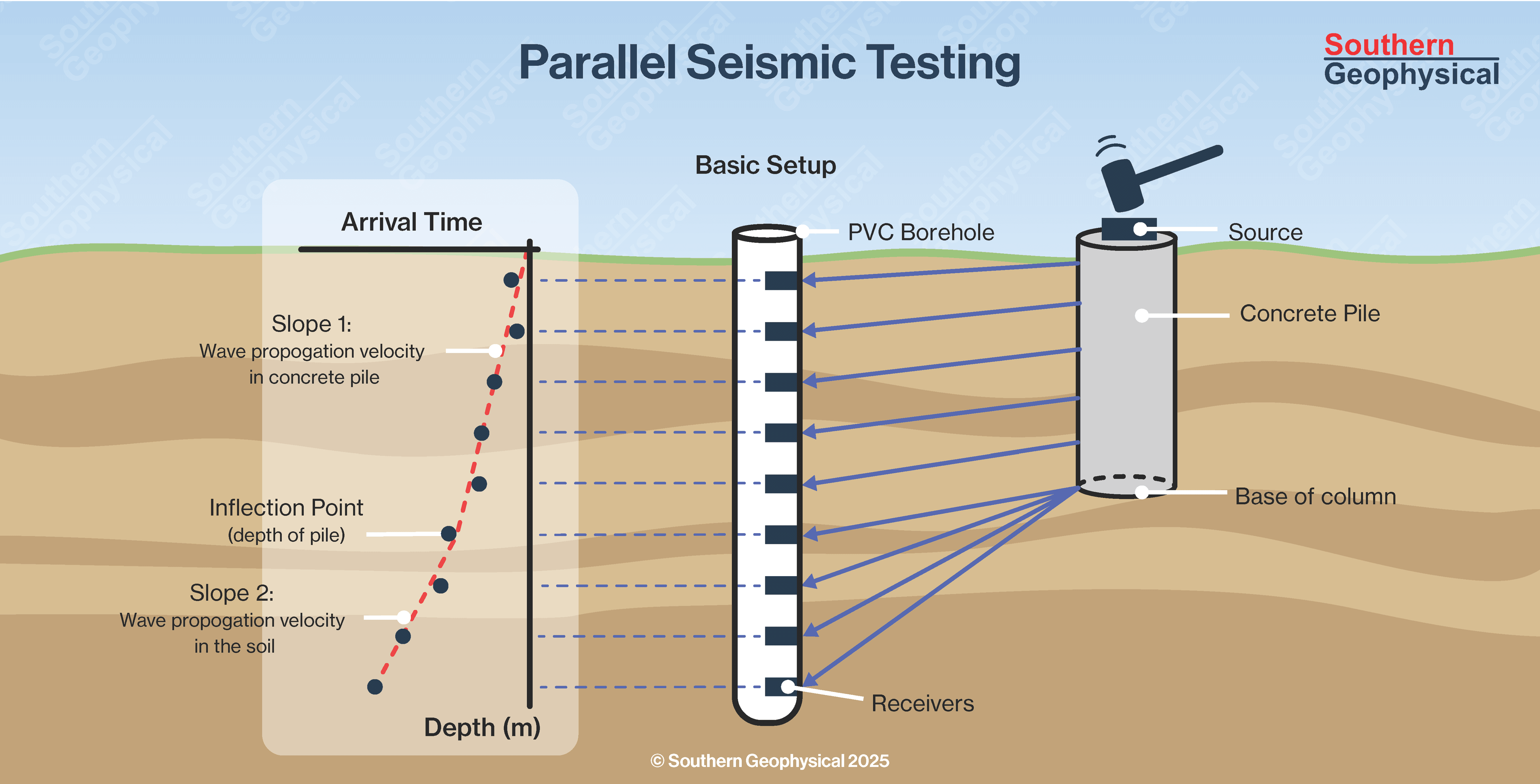
Parallel Seismic Testing (ASTM D8381)
Parallel Seismic testing is a reliable method when low strain pile testing methods cannot be implemented due to inaccessibility. Parallel Seismic testing is used to determine lengths of deep foundations where access to the pile heads is obstructed. This method involves drilling a borehole and installing a 50mm PVC lined tube next to the pile to be tested (within 2m) and protruding at least 3 meters below the estimated pile toe. A triaxial geophone is lowered down the borehole and the structure above the pile head is impacted with a specialised hammer. The arrival time of the P-wave energy at the geophone allows the depth of the pile to be calculated.
How can we help?
Fill in the contact form below. We respond to all weekday enquiries within 24 hours



